- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 88 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-16 Origin: Site
Terminal block also known as a connection terminal, is a modular block used in electrical and electronics systems to connect and secure electrical wires or cables. It serves as a convenient and organized way to make electrical connections, for power distribution, signal routing, or control wiring. Terminal blocks work by guiding electrical current through an insulated structure, enabling multiple wires to operate concurrently in close proximity. When you need electrical wires to connect, a terminal block provides a safe, convenient way to keep them organized.why not just solder them together? Or twist them together and wrap them with electrical tape?
Using terminal blocks is a much better solution for connecting wires. Choise the right terminal block can help you save 35%-40% cost and time! You can send us email for getting guides of choices in any time ! sophia@cnsyelectronics.com.We`ll show you more good reasons to use terminal blocks in this article.
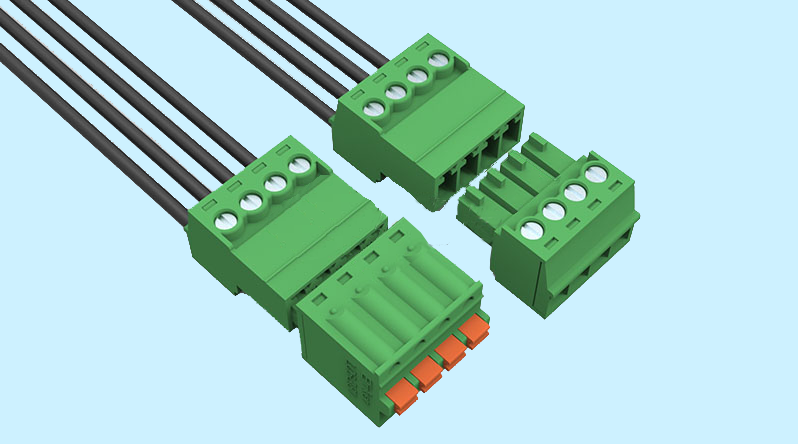
What are electrical terminals used for?
Electrical Terminals are a class of electrical connector which are used to transfer electrical current from a power or grounding source to a use. With the Terminal blocks increasing safety by grounding, isolating, and protecting the other components in the electrical circuit. Terminal blocks are available with finger-safe connections to prevent electrical shock. And, terminal blocks can also provide test points, which add even more safety to the circuit.
How to select a terminal block?
A good rule of thumb is to select a terminal block that has a current rating of at least 150% of the system's expected maximum current. The voltage rating should also be greater than the maximum system voltage. When thinking about this, voltage surges must be taken into consideration to prevent damaging the connection.
What is terminal block in control panel?
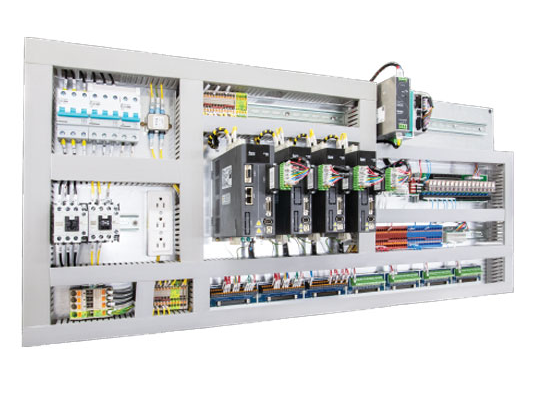
Terminal blocks were originally referred to as screw terminals because a screw was used to secure wires to a conducting plate, making an electrical connection. In control systems, terminal blocks are used to connect panel-mounted equipment to power and field wiring.
You can find dozens of types of terminal blocks, some generic, some specialized. Designers have developed terminal blocks for household, industrial, electronic, and many other uses.
· Dual-Level Terminal Blocks: Dual-level terminal blocks have an additional level of connection terminals stacked above the first one. This arrangement is commonly employed to save space while maintaining functionality.
· Three-Level Terminal Blocks: Similar to dual-level blocks, three-level terminal blocks have an extra level at the top. One of the advantages of using multi-level blocks is the ability to make multiple connections within the same block, offering increased versatility and compactness.
· Screw clamps: Screw clamps are the industry standard for termination methods. They use screws to tighten the wires and accommodate a variety of wire sizes. They are commonly used in home and commercial wiring for moderate voltage and current needs. Care must be taken not to overtighten as this may damage the cable and cause an unreliable connection.
· Spring Clips: Spring clips use spring force to secure wires. They are a newer alternative to screw clamps and are particularly suitable for applications with limited workspace and smaller wire diameters.
· Fence terminals: Similar to screw terminals, fence terminals use screws to secure the cable. They usually have multiple terminal points and small obstacles between the various terminals. Barrier terminals are suitable for high-voltage scenarios where arcing or short circuits need to be prevented.
· Push-In Terminals: Push-in terminal blocks use spring-loaded levers that allow cable entry in one direction and prevent disassembly, with the added benefit of preventing over-tightening. However, some may not be reusable and lack disassembly mechanisms, which may pose a challenge for repair efforts.
· Pluggable Terminal Blocks: Pluggable terminal blocks feature cable entries and plug outputs for easy connection to an outlet. They are useful for hot-swappable or removable connections during repair or inspection. Screw contacts with metal plates for holding cables of various sizes are common in pluggable terminal block.
· Din Rail Mount Terminal Blocks :DIN rail refers to a mounting system in the form of globally standardized long metal strips used to attach electrical and industrial control products in equipment cabinet racks. The DIN Rail itself is a mechanical component support with no connective or conductive capability.
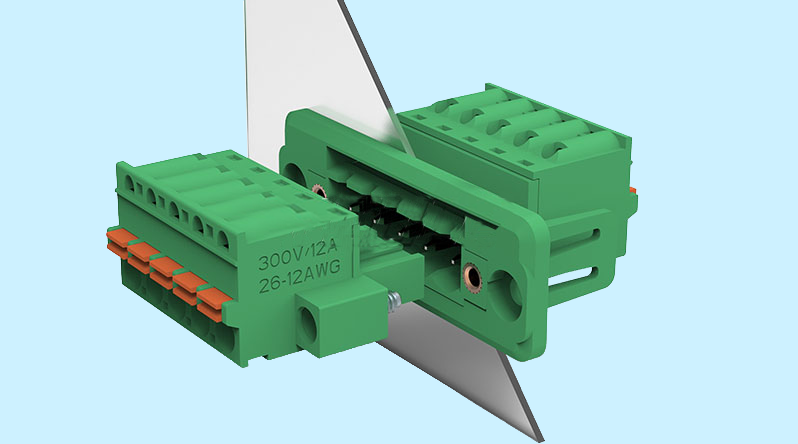
Organize the wiring to improve panel space:Terminal strips provide a space-saving solution by allowing for a tidy and organized arrangement of wires. This makes it easier to access the wires when necessary, while also freeing up valuable panel space.
Simplify assembly methods:Terminal strips simplify the assembly process by providing a quick and easy way to connect wires. This reduces the risk of errors during installation and also saves time and effort.
Improve the electrical safety of the panel:Terminal strips help to improve electrical safety by reducing the risk of exposed wires, short circuits, and electrical shocks. They also help to prevent wiring errors, which can lead to dangerous electrical situations.
Facilitate equipment maintenance and problem detection:Terminal strips make it easy to access and troubleshoot wires, which facilitates equipment maintenance and problem detection. This helps to reduce downtime and increase productivity, as well as making it easier to replace faulty components or upgrade equipment.
Choosing the right terminal block requires considering some key factors and selecting based on the application.
Current requirements:Determine the required current rating and choose a terminal block that can handle the expected current demand, while also considering the need for a safety buffer. Generally, it is recommended to choose a terminal block with a current rating higher than the actual current requirement to prevent overheating and damage to the terminal block.
Voltage requirements:Determine the required voltage rating and choose a terminal block that can handle the expected voltage demand. Additionally, pay attention to the insulation performance of the terminal block to ensure effective isolation between different circuits.
Wire type: Different types of wires have their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to choose the appropriate wire type based on the application.
Installation method:Different terminal blocks have different installation methods, includingPCB mount,barrier strips, andfeed-through.
Terminal block size:Determine the required terminal block size to ensure that it can accommodate the wires being used and the appropriate terminal blocks.
How to install terminal blocks?
you can reference this datesheet picture
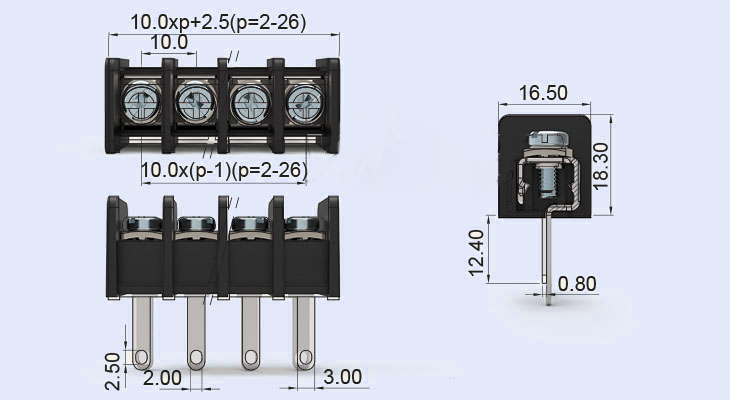
Installing barrier terminal blocks requires attention to detail, the right tools, and a solid understanding of your electrical system’s specifications. Follow this refined step-by-step process to ensure a reliable and standards-compliant installation.
Begin by reviewing the technical specifications of your application, including operating voltage, current rating, and wire gauge requirements. Choose a barrier terminal block that meets or exceeds these parameters. For example, applications involving up to 600V or currents above 30A may require a double-row or high-amperage model. Verify compliance with UL 1059 or IEC 60947 standards as applicable.
Carefully strip the insulation from each wire using a precision wire stripper, removing only the recommended length—typically between 6 to 10 mm. Avoid damaging the wire strands, as this may reduce conductivity and increase the risk of connection failure or electrical arcing.
Insert each stripped wire into the designated terminal chamber. Use a calibrated torque screwdriver to tighten the terminal screws to the manufacturer’s specified torque—commonly in the range of 0.5 to 2.5 Newton-meters. Applying the correct torque ensures a secure electrical connection while preventing damage to internal components.
Once all connections are completed, use a digital multimeter or continuity tester to verify electrical integrity. Confirm that each terminal connection is secure and that insulation resistance between adjacent terminals meets safety standards. This final step ensures system reliability and user safety before energizing the circuit.
This refined procedure not only enhances safety and performance but also aligns with best practices followed by certified electricians and control panel integrators. Proper installation extends product lifespan and significantly reduces the risk of downtime or electrical hazards.
Connecting a wire to a screw terminal block is a fundamental skill in electrical wiring, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.

Before making any connection, the wire must be properly prepared. This involves carefully stripping the insulation from the end of the wire using a wire stripper. The length of the bare wire exposed is critical; it should be just long enough to make full contact with the metal conductor inside the terminal block, typically indicated by a strip length guide on the block itself.
If the bare wire is too long, it risks touching an adjacent terminal or exposed components, leading to a short circuit. If it’s too short, it won’t make adequate contact, resulting in a poor connection or overheating.
Once the wire is prepared, use the appropriately sized screwdriver to loosen the screw on the screw terminal block. You’ll typically need to turn it counter-clockwise until the clamping plate or yoke underneath the screw lifts or opens sufficiently to allow the wire to be inserted.
Insert the prepared, bare end of the wire fully into the opening beneath the screw or clamping plate. Ensure that all strands are neatly contained within the terminal and that the insulation abuts the entry point of the terminal block, leaving no bare wire exposed outside the terminal’s housing.
After the wire is correctly positioned, use the screwdriver to tighten the screw firmly in a clockwise direction. As you tighten, the screw will press down on the clamping plate or directly onto the wire, creating a secure mechanical and electrical connection.
It’s crucial to tighten until the wire is held firmly and cannot be easily pulled out with a gentle tug. However, avoid overtightening, as this can strip the screw threads, damage the wire (especially smaller gauges), or crack the terminal block’s housing. A properly tightened screw connection ensures low resistance and prevents loosening due to vibration or thermal cycling over time.
The final and essential step is to verify the integrity of the connection. Gently pull on the wire to ensure it is securely clamped and cannot be easily dislodged. This mechanical check helps confirm that the screw has adequately gripped the wire.
For a more thorough check, if safe to do so with power off, use a multimeter in continuity mode to confirm a low-resistance electrical path between the newly connected wire and its corresponding point on the circuit.
Shanye(KEFA)’s lighting connectors are the perfect link between solid and fine-stranded conductors. Their approval as independent equipment per EN 60998, so,its lighting connectors can be used in nearly all household applications and similar building installations where a connection between solid and fine-stranded conductors is required.Benefits:Ideally connect solid conductors with fine-stranded conductors.Simple, tool-free wiring – especially helpful for overhead work.Support numerous applications, including connecting devices with fine-stranded conductors to fixed installations blinds motors.
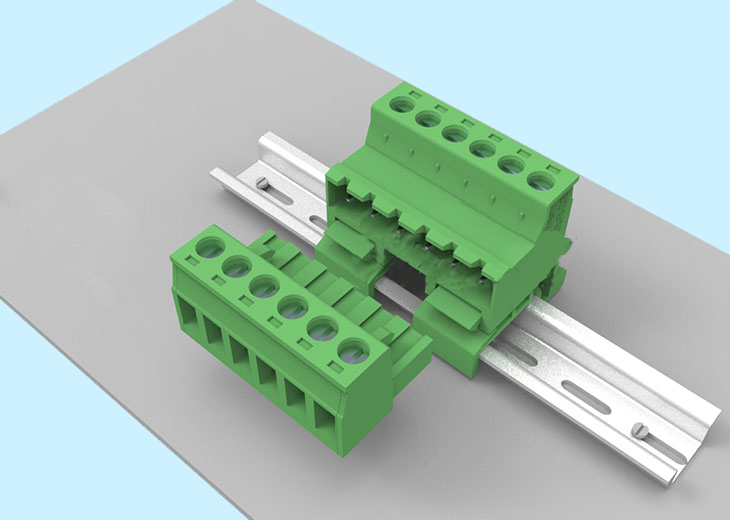
Din Rail-Mount Terminal Blocks with Push-in reliability have a large range of cross-sections, offering the right terminal block for all building applications. With the demands on buildings constantly increased and change, Din rail terminal block enables future-proof installation.
Benefits:Flexible selection of the actuation variant (operating slot, push-button or hybrid).Standards-compliant insulation resistance measurement thanks to reliable, convenient N-disconnect variants.Push-in termination of solid conductors and fine-stranded conductors with ferrules.Sufficient wiring space thanks to compact design.Three-line custom labeling via marking strips provides clear organization – even when wired.
FAQ
Q:Why use terminal blocks instead of directly splicing wires?
A:While splicing wires might seem like a quick fix, terminal blocks offer critical advantages that professionals rely on
Q:Are terminal blocks necessary for all electrical connections?
A:No, terminal blocks are not always necessary, but they are highly recommended for:High-current circuits,Frequent wire changes.Safety-critical systems .
Q:Can terminal blocks be reused?
A:Yes, of course,most terminal blocks can be reused by simply loosening the screws or releasing the clamps to disconnect and rewire as needed.
Q:How do terminal blocks improve electrical safety?
A:Terminal blocks enhance electrical safety by providing secure, insulated connections that prevent loose wires, short circuits, and accidental contact, while enabling easy maintenance and compliance with safety standards.
Q:Can terminal blocks be used in outdoor environments?
A:Yes, terminal blocks can be used outdoors if they are specifically rated for outdoor use (waterproof, UV-resistant, and corrosion-proof models with IP68/IP67+ protection).
Q:Do I need special tools to install terminal blocks?
A:No need, most terminal blocks only require a standard screwdriver, but spring-clamp types may need a release tool for easier wiring.
Q:How do I calculate how many terminal blocks I need?
A:Count the number of wire connections in your PCB Board circuit, then choose terminal blocks with enough poles.
Q:What are the red flags when buying cheap terminal blocks?
A:Avoid cheap terminal blocks with loose contacts, thin plastic insulation, without approved certifications, or screws that strip easily—they risk overheating and connection failures.
Ready to upgrade your electrical connections? Browse our selection of high-quality terminal blocks or contact our experts for personalized advice.
A terminal block is a compact, insulated base with metal contacts that lets you clamp, join, and distribute conductors without soldering. If you’ve ever routed power to a drive, brought sensor leads into a controller, or handed off field wiring to a PCB, you’ve used one. Understanding what is a term
As a Engineer ,It is very important to choose globally recognized premium terminal blocks .these manufacturersas below: Phoenix Contact, WAGO, Weidmüller, Eaton, Molex, Amphenol, Harting, and Shanye Electronics (subsidiary of Kefa Electronics). These industry leaders collectively dominate the $4.6
This article covers the technical features of spring-loaded and push-in terminals, and both the advantages and disadvantages of these technologies when it comes to installation practices, commissioning, footprint and authorisation for the North American market. Why do we need spring terminal block ?
Wiring a terminal block correctly is a fundamental skill in electrical work, ensuring safe and reliable connections. This article will help you to understand the essential steps, from preparing your wires to securing them properly within various terminal block types.ContentWhat are Terminal Blocks?R
What is terminal block ?terminal block, also known as a connection terminal, is a modular block used in electrical and electronics systems to connect and secure electrical wires or cables. It serves as a convenient and organized way to make electrical connections, whether for power distribution, sig
Terminal electronics is the key point at which a conductor from a electronic component, device or network comes to an end.Terminal may also refer to an electrical connector at this endpoint, acting as the reusable interface to a conductor and creating a point where external circuits can be connected